Files storage: Add or edit permissions
Permissions will allow or restrict end users to perform actions on files and folders.
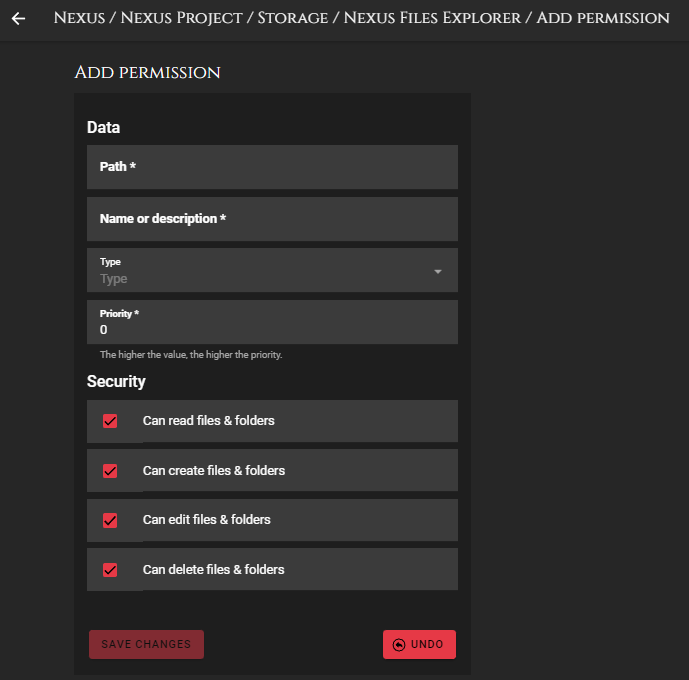
Form fields
- Path: Path of the permission. It accepts wildcards.
- Name: Name or description of the permission. This will help you to identify it easily.
- Type: Permission type.
- Priority: Priority of the permission. Permissions work like hierarchies. All of them are linked. The priority is used to know in which position the permission should be, since permissions with higher priority can override those with lower priority. The higher the number, the higher the priority.
- Security: Restrictions and allowances that will apply to the permission (read, create, edit, delete).
Permission types
Permission types are filters that are used when applying allowances and restrictions. They are combined with a wildcard to determine which users or credentials the different permissions correspond to.
- Credentials
- Users
Examples
Example 1
Everyone can read (R), create (C), edit (E) and delete (D) any file or folder.
| Path | R | C | E | D | Type | Filter | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ** | V | V | V | V | User | * | 0 |
Example 2
Credential key "admin" can read, create, edit and delete any file or folder. Credential key "basic" can read only files in "public" folder.
Let's make it step by step.
Step 1: Add a restriction so that no one has permission to do anything with any files and folders.
| Path | R | C | E | D | Type | Filter | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ** | X | X | X | X | Credential | * | 0 |
Step 2: Add the "admin" permissions. This will override the previous one only for the applied filter.
| Path | R | C | E | D | Type | Filter | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ** | X | X | X | X | Credential | * | 0 |
| ** | V | V | V | V | Credential | admin | 1 |
Step 3: Add the "basic" permissions.
| Path | R | C | E | D | Type | Filter | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ** | X | X | X | X | Credential | * | 0 |
| ** | V | V | V | V | Credential | admin | 1 |
| */public/ | V | X | X | X | Credential | basic | 2 |